Consensus Mechanisms Explained: PoW Vs. PoS
Consensus mechanisms in cryptocurrency: Understanding work (POW) and evidence of a proportion (pos)
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum and others, are digital or virtual currencies that use encryption for safety and decentralized control. In order to maintain the integrity of these cryptocurrencies, it is essential for a consensus mechanism that is necessary to validate the transactions and the appropriate blockchain for all participants.
In this article, we will deepen the two most common consensus mechanisms used in cryptocurrency: proof of work (POW) and PANDEMENT (POS).
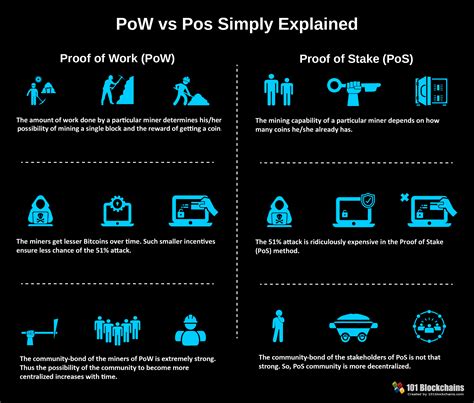
Certificate of Work (POW)
A certificate of employment is one of the earliest and most commonly used consensus algorithms. For the first time in 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto introduced it as a solution to the difficulty problem of the Bitcoin mining process.
This is how Pow works:
- Mining workers compete : Mining workers compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles that require significant computational force.
2
- Validation : The validate (miners) of the puzzle has greater opportunities to choose to create new blocks, which they then send to the network.
- Energy consumption : Solving Pow puzzles requires significant computational force, which can lead to high energy consumption and environmental pollution.
Example: Bitcoin Mine
Let’s look at an example to illustrate how POW works, let’s look at:
- Solution of the puzzle : The miner resolves a complex mathematical puzzle that requires 100 million calculation cycles.
- Awards
: The miner can create new transaction blocks and send them to the network.
- Energy consumption : The miner has spent about 10 minutes of electricity to solve the puzzle.
Reservation (POS)
Proof is a consensus algorithm introduced in 2014 by Satoshi Nakamoto as an alternative to POW. It is designed to be more energy efficient and environmentally friendly.
This is how POS works:
- Stakeholders participate : Anyone who owns or has a certain amount of cryptocurrency may be on their coins.
2
- Panes are burned : Validates with higher stakes have more opportunities to choose to create new blocks that they then send to the network.
- Energy consumption : Creating a new block in POS requires less computational force compared to POW.
Example: Ethereum’s gas -based validation
Let’s look at an example of how pos works in Ethereum, consider:
- PLAYING AND VALIDE : Anyone who owns or has a certain amount of Ethereum may be on their coins.
2
- Gas based validation : A valider with the largest gas threshold to create new blocks will get a new block creating.
- Energy consumption : Creating a new block in POS requires less computational force compared to POW.
conclusion
In summary, both work certificates (POW) and Panosto (POS) are widely used for cryptocurrency consensus mechanisms. Although Pow was the original solution introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008, POS has gained popularity due to potential energy efficiency and environmental durability.
However, it is imperative to note that both algorithms have limitations and vulnerabilities. For example, Pow is susceptible to Asic (an application -specific integrated circuit) for mining, while POS can be prone to 51%attacks if one entity dominates more than half of the share.